Structure-based drug discovery
In our drug discovery projects, we target enzymes involved in diseases using protein structure knowledge for designing inhibitors. We also employ fragment-based drug discovery to find small molecules that disrupt protein-protein interactions in hematological malignancies.
Contact:
Jiří Brynda, Matúš Drexler, Petr Pachl, Klára Pospíšilová, Pavlína Maloy Řezáčová, Václav Veverka
Human carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
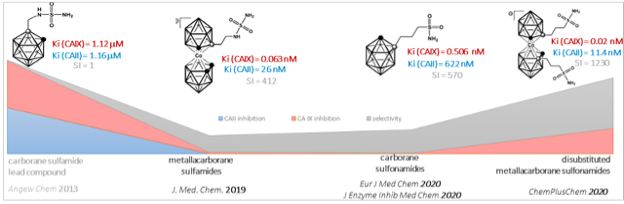
Our main focus is on human carbonic anhydrases (CA), which have significant roles in physiological and pathological processes, making them potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets. We specifically aim to develop selective inhibitors for the tumor-specific CA IX isoform. Recently, we completed a project on carborane inhibitors for tumor-specific CA IX. These novel inhibitors combine a bulky inorganic cluster with an alkylsulfamide or alkylsulfonamide group, resulting in potent and selective inhibition. Preclinical studies demonstrated low toxicity, favorable pharmacokinetics, and the ability to reduce tumor growth. Cluster-containing inhibitors of CA IX show promise as candidates for drug development and/or combination therapy in boron neutron capture therapy.